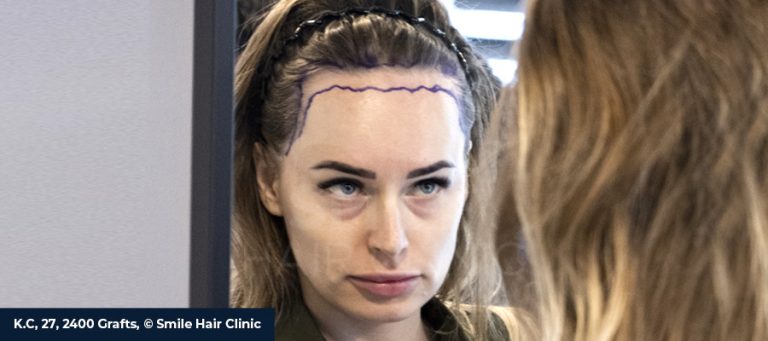
Hair loss is a common issue that many women experience at some point in their lives. Women are more affected by hair loss than men, as the ideals of female beauty and sophistication are aimed at them both verbally and nonverbally. While it is socially acceptable for men to experience hair loss, women who experience thinning hair may feel as though they are alone in the world because flowing hair is often associated with feminine beauty. Since not many women lose their hair, a woman with hair loss may feel like an outcast. As a result, women may experience psychological and emotional difficulties because of their hair loss. Maintaining the ideal level of thick hair in society becomes more challenging when social media strongly influences people’s perceptions of themselves.
However, it’s a problem that can be addressed with women’s hair loss therapy. Several therapy approaches, including FUE hair transplantation, have demonstrated significant promise in treating irreversible hair loss and giving women their hair back, along with their confidence!
Reasons Why Women Lose Their Hair
Alopecia Androgenetica (AGA):
Male-patterned hair loss, or androgenetic alopecia, is the most prevalent type of hair loss in both men and women (AGA). Women mostly experience it after the age of 40, particularly around menopause, when hormones are already fluctuating wildly. Unfortunately, there are lots of women who start to suffer from AGA in their early twenties. The progressive weakening and thinning of hair in the front is the first sign of AGA in females. The main factor in this hair loss is testosterone, a hormone generated by the adrenal gland and ovaries. Although testosterone is produced considerably less in women than in males, it can still undergo 5-alpha-reductase and transform into its metabolite, dihydrotestosterone (DHT), responsible for thinning and hair loss. Women will experience fewer severe side effects at first than men since they manufacture less 5-alpha-reductase.
Changes in Hormones:
Hormone levels play a significant role in women’s journeys through life, such as menopause, childbearing, and the onset of menstruation. Hormone fluctuations, the negative effects of birth control drugs, and illnesses like thyroid disease can all cause hair loss. These hormone changes can disrupt the normal cycle of hair growth, causing thinning and shedding.
Traction Type Alopecia:
When tight hairstyles like braids, buns, and ponytails harm hair follicles, traction alopecia occurs. Wearing a tight braid or ponytail regularly can damage the hair follicles and break hair, leading to long-term hair loss and thinning. Ignoring them could cause irreversible harm, including hair loss.
Iron deficiency anaemia:
Low iron is one of the most frequent reasons women experience hair loss. A woman loses iron every time she has her period; if she does not consume enough red meat, which is high in iron, her hair will suffer. Iron deficiency can lead to hair shedding and a reduction in the strength of the hair follicles. Iron deficiency-related hair loss typically disappears when the body receives more of this nutrient, sometimes through supplements and other means, including diet.
Adverse effects of medication:
It could occasionally be an adverse effect of prescribed drugs. Hair thinning can be caused by certain medications used to treat depression, gout, cancer, hypertension, arthritis, and heart disease. Consequently, individuals experiencing medication-induced hair loss should also consult their physician.
Emotional trauma and stress:
Stress is another important factor in female hair loss. Excessive anxiety or hair loss following abrupt emotional shocks can also result in hypotrichosis. These conditions can affect the scalp, eyelashes, and eyebrows. Although it usually requires medical attention as well, stress-related hair loss can occasionally compel you to seek psychological support.
Inadequate Nutrition and Unhealthy Diet:
Dietary irregularities or abrupt changes have a significant impact on hair. As is well known, low nutritional levels, especially those of the micronutrients needed for healthy hair growth (such as vitamins A, D, and E) or minerals like iron and zinc deficiency, can also lead to thinning hair. Minerals and vitamins are crucial for maintaining hair health; therefore, eating a balanced diet that includes proteins can help maintain the health of natural hair.
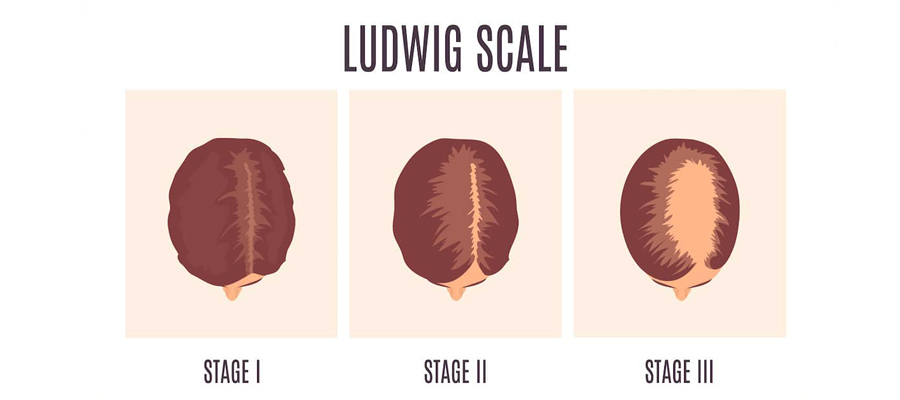
Women’s Hair Loss: Staging
The most often used classification scheme for female hair loss is the Ludwig Classification. According to this classification, hair loss is symmetrically divided into three primary grades:
Grade 1: Moderate thinning visible on the vertex area of the scalp.
Grade 2: Thinning becomes more pronounced, and the affected area is clearly noticeable.
Grade 3: Extensive thinning across the top and crown regions of the scalp.
This classification system aids medical professionals in determining the appropriate course of action for treating patients by helping them assess the severity of their hair loss issues.
Diagnosis of Female Hair Loss
This is in contrast to the pattern of loss seen in males with male-pattern baldness, which starts at the crowns and temples and progresses toward the back of the head, creating a structure like a horseshoe where the remaining hair wraps around the back of the neck and behind the ears. Even while women seldom go as bald as men, it is just as painful when the thinning is noticeable. Men are more likely to be diagnosed with hair loss than women because a number of factors need to be considered in the latter case.
Methods of Diagnosis:
It is typical for women to get a blood test to rule out any underlying health issues, such as thyroid disorders, hormonal imbalances, or anaemia that could be brought on by hair loss.
Scalp analysis A microscopical examination of the scalp can be used to identify anomalies and see the hair follicles.
Pull Test: To determine how many hairs come out, gently pull out a bunch of hairs. You may be experiencing hair loss if you lose a lot of hair.
Biopsy: Occasionally, a tiny sample of your scalp for more detailed analysis might be beneficial to ascertain whether or not the hair follicles are in good health and are not being attacked by conditions that impact the hair itself.
A phototrichogram is a method of taking consecutive pictures of the scalp to track hair growth or loss over time, indicating the progression of hair loss.

Options for Women’s Hair Loss Treatment
While treating the hair loss of adult women can be more challenging than that of males, there are methods to slow down or even stop the process and occasionally regrow hair. The earlier the treatment is initiated, the more successful the outcomes.
Medical Interventions:
Prescription drugs, such as finasteride and minoxidil, can be used to treat women with androgenetic alopecia. The reason finasteride stops hair shrinkage is because it prevents DHT from being formed. Although there is some evidence to support the possibility of dry skin and decreased sex drive, these are very uncommon problems.
Low Laser Treatment:
Low-level laser Therapy, or LLLT, is a noninvasive procedure that uses laser light to stimulate hair follicles and improve blood flow to the scalp. This method is not a baldness cure, but it can help maintain existing hair and slow down the rate of hair loss.
Mesotherapy:
Mesotherapy: To nourish hair follicles, vitamins, minerals, and enzymes are injected into the scalp using tiny needles. This technique helps to strengthen existing hair and promote hair growth. Most of the time, this medication is utilized in addition to other therapies.
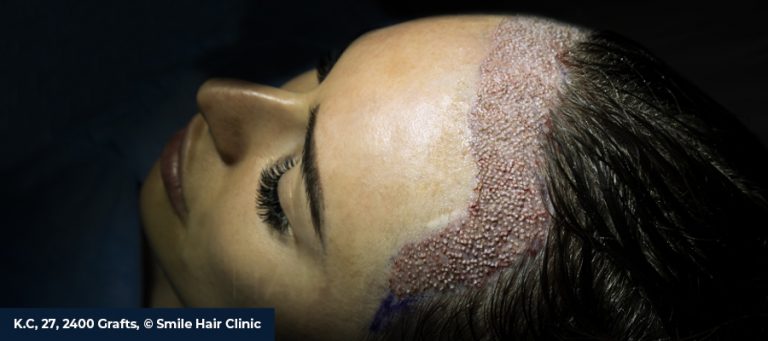
Hair Transplantation Using FUE
Hair transplantation with FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) can offer a permanent option for women experiencing moderate to severe hair loss. Moving healthy hair follicles from one area—usually the back of your head—to areas with less or no hair is a surgical hair restoration treatment. The Sapphire FUE Hair Transplant is a cutting-edge procedure that uses sapphire blades to make clean incisions that speed up healing and produce results that seem more natural. It is available at our Smile Hair Clinic. Hair transplantation for women involves customizing an aesthetic therapy that requires meticulous preparation and focused attention to both the physical and emotional aspects of hair loss.
What We Can Provide for You
Women who lose their hair may find it distressing, but it is treatable with the correct diagnosis and care. Our skilled surgeons, who specialize in FUE hair transplantation, have carried out thousands of successful hair restoration procedures for individuals from various nations across the world.
To receive extra guidance on hair loss, schedule a complimentary online consultation with one of Smile Hair Clinic’s surgeons. They can provide you with information on the most suitable treatment choices. Our staff will assist you in selecting from our available prescription drugs, laser therapy, and hair transplants.
We deliver the innovative Sapphire Hair Transplantation for people whose hair loss is naturally resistant to treatment. This top-rated therapy produces impressive results for women with permanent hair loss. Our team of skilled surgeons will ensure you feel secure and well-supported throughout the process.
Female hair loss is a common issue that requires special attention. If hair loss is identified early on and treated quickly, it can reverse both hair loss and growth. Discover the best new hair for regaining confidence with medicinal treatments, mesotherapy procedures, and surgical solutions like FUE transplantation for ladies.