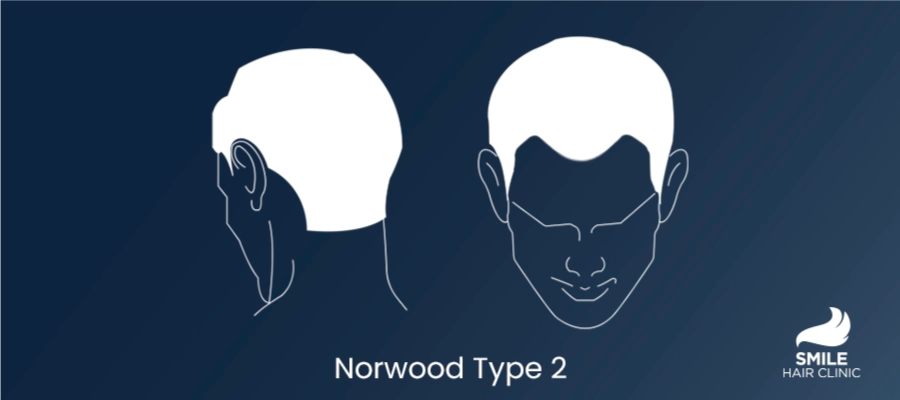
Norwood Type 2 Hair Loss
Norwood Type 2 hair loss is an early stage of male pattern baldness. This stage is characterized by a moderate recession of the hairline, particularly at the temples. It is crucial for individuals experiencing this type of hair loss to explore various treatment options before considering a hair transplant. Early intervention can often slow the progression of hair loss and improve hair density.
Norwood Type 2 hair loss is defined by a receding hairline at the temples, creating a noticeable “M” shape. This stage marks the initial visible signs of androgenic alopecia, a condition driven by genetic and hormonal factors, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT). The recession at this stage is moderate and may not be immediately noticeable, but it signals the beginning of more significant hair thinning if left untreated.
Causes of Norwood Type 2 Hair Loss
This type of hair loss predominantly affects men, although women can also experience similar thinning patterns. The condition is largely hereditary, with those having a family history of hair loss being more susceptible. Androgens, especially DHT, play a significant role in the progression of hair loss by binding to hair follicles and causing them to shrink. Over time, this process, known as miniaturization, leads to thinner, shorter hairs and eventually dormant follicles that no longer produce hair.
Diagnosing Norwood Type 2 hair loss involves a clinical examination and an assessment of the patient’s hair loss pattern. The Norwood-Hamilton Scale is a standard tool used to classify the extent of male pattern baldness, which helps determine the most appropriate treatment strategies.
Norwood Scale Overview
- Norwood Type 1: Minimal or no hairline recession.
- Norwood Type 2: Noticeable recession at the temples, forming an “M” shape.
- Norwood Type 3: Deeper temporal recession and early thinning on the crown.
- Norwood Type 4: Further recession and extensive thinning on the crown.
- Norwood Type 5: Merging of the temple and crown thinning.
- Norwood Type 6: Loss of the bridge of hair between the temple and crown.
- Norwood Type 7: Extensive hair loss, leaving only a band around the sides and back of the scalp.
Differentiating Type 2 from Other Types
Norwood Type 2 hair loss is distinct due to its specific pattern of hairline recession at the temples, forming an “M” shape. This stage is an early indicator of male pattern baldness and differs from more advanced stages, which involve significant thinning and bald patches. Proper identification of this stage is essential for implementing effective treatment strategies early on.
Treatment Options
Medications
Several medications can help manage Norwood Type 2 hair loss:
- Minoxidil: We still do not know the exact way how minoxidil boost hair growth; but an oral or topical treatment that stimulates hair growth and slows hair loss. Taking a pill in the morning or applied directly to the scalp, minoxidil has a great impact on hair density and thickness. Available in 2% (for female) and 5% (for male) formulations, it is often the first line of defense against early hair loss. Bıut you should keep in mind if you start to use minoxidil it is better to continue it otherwise your hair may turn to its earlier look easily.
- Finasteride: An oral medication or topical spray that reduces DHT levels, thereby slowing hair loss and promoting hair regrowth. Finasteride effects by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, decreases the conversion of testosterone to DHT, which helps in maintaining hair density and reducing hair follicle miniaturization.
Surgical Procedures
For those who do not respond to medical treatments or have more advanced Type 2 hair loss, surgical options like hair transplantation may be considered.
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): This procedure starts with removing a part of the skin (“strip” ) of from the donor zone (usually the back of the head, a zone like horse shoe) and sperating it into individual follicular units for transplantation. While FUT can leave a linear scar, it allows for better success with Afro-textured hair.
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): This technique involves individually harvesting multipl hair in single groups ( follicular units ) from the donor zone and implanting them to bald zones or the thinning areas. FUE does not result in a linear scar and has a shorter recovery time, most of the leading clinics prefer this technique.
Healthy Lifestyle and Taking Care Of your Body
In addition to medical and surgical treatments, certain lifestyle changes and taking care of your body can help manage hair loss:
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a healthy diet rich in, essential proteins, vitamins and minerals that support hair health, such as red meat, biotin, vitamin D, and zinc, can promote stronger hair growth.
- Scalp Care: Regular scalp massages improves micro circulation to the hair follicles, potentially promoting hair growth. Keeping the scalp clean and free of inflamation (dandruff) is also important for maintaining healthy hair.
- Hairstyles: Choosing hairstyles that make thinning hair less noticeable can improve one’s appearance and confidence. Short, close-cut styles or even shaving the head can minimize the appearance of hair loss, while certain styles can add volume or cover thinning areas effectively.
Norwood Type 2 hair loss is an early stage of male pattern baldness that can be effectively managed with early intervention. Ongoing research into the genetic and hormonal factors contributing to hair loss will continue to improve treatment options and outcomes for patients. Advances in diagnostic tools, such as dermoscopic imaging, will aid in developing personalized treatment plans.
Future studies may focus on new medications that more effectively target the causes of hair loss, potentially preventing its onset altogether. Innovations in hair transplantation techniques could also enhance the natural appearance and longevity of transplanted hair. Understanding the genetic basis of hair loss will be crucial for developing more specific and effective treatments, offering hope for better management and prevention strategies.
In summary, Norwood Type 2 hair loss is a common but manageable condition. Through a combination of surgical, medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and surgical options when necessary, individuals can effectively address their hair loss and maintain a healthy, natural appearance. Early treatment is key to achieving the best outcomes and preventing further progression of hair loss.